Quantitation of N'-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in smokers' urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Michael Urban, Gerhard Scherer, Dominique Kavvadias, Heinz-Werner Hagedorn, Shixia Feng, Richard Serafin, Sunil Kapur, Raheema Muhammad, Yan Jin, Paul Mendes, Hans Roethig
Index: J. Anal. Toxicol. 33(5) , 260-5, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The tobacco-specific nitrosamine N'-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) is carcinogenic to humans (IARC Group 1). Assessing the tobacco smoke-related exposure to NNN by suitable biomarkers is of interest for risk evaluation. Recently, NNN and NNN-N-glucuronide have been quantified in urine of smokers. However, it is unknown what percentage of the absorbed dose of NNN is excreted as total NNN (sum of free and conjugated NNN) in urine of smokers. We developed a sensitive method based on liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry with deuterium-labeled internal standard for the determination of total NNN in human urine. The limit of quantitation of the method was 2 pg/mL with a calibration line linear up to 256 pg/mL. In a study with 16 smokers in which the respiratory retention of NNN was measured through controlled smoking, we found that on average about 1% of the pulmonary NNN dose was excreted in 24 h urine as total NNN.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
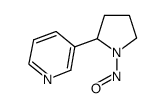 |
rac N'-Nitrosonornicotine
CAS:80508-23-2 |
C9H11N3O |
|
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation dynamics during earl...
2014-12-01 [PLoS Genet. 10(12) , e1004868, (2014)] |
|
Tobacco-specific N-nitrosamine exposures and cancer risk in ...
2014-05-15 [Int. J. Cancer 134(10) , 2278-83, (2014)] |
|
Evidence supporting product standards for carcinogens in smo...
2015-01-01 [Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 8(1) , 20-6, (2015)] |
|
Three nicotine demethylase genes mediate nornicotine biosynt...
2010-01-01 [Phytochemistry 71(17-18) , 1988-98, (2010)] |
|
Nornicotine nitrosation in saliva and its relation to endoge...
2013-02-01 [Nicotine Tob. Res. 15(2) , 591-5, (2013)] |