| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
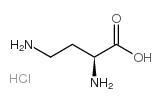 |
H-Dab.HCl
CAS:1482-98-0 |
|
 |
PACAP(6-38), human, ovine, rat
CAS:137061-48-4 |