An evaluation of a new lactic acid polymer drug delivery system: a preliminary report.
Y Sawada, T Ohkubo, M Kudoh, K Sugawara, K Otani, J Sasaki
Index: Br. J. Plast. Surg. 47(3) , 158-61, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A new drug delivery system, made of a mixture of DL-lactic acid polymer and a copoly (L-lactic acid/delta-valerolactone) polymer (LAP) containing varying concentrations of Ofloxacin, has been evaluated. Results revealed that a LAP drug delivery system containing 0.03% Ofloxacin inhibited the in vitro growth of clinically derived Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Further, in an in vivo situation in rats, at 1 week after the wound was inflicted, no infection was macroscopically seen in split-thickness wounds that had been covered by LAP drug delivery system containing 0.5 or 0.03% Ofloxacin, and more than 80% of the wound area had epithelialised.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
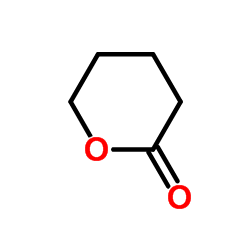 |
delta-Valerolactone
CAS:542-28-9 |
C5H8O2 |
|
Antimicrobial properties of Kalanchoe blossfeldiana: a focus...
2015-07-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67 , 951-62, (2015)] |
|
Characterization of the PON1 active site using modeling simu...
2008-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 7504-9, (2008)] |
|
5- and 6-membered (thio)lactones are prodrug type carbonic a...
2012-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22 , 267-70, (2012)] |
|
High affinity, stability, and lactonase activity of serum pa...
2005-09-06 [Biochemistry 44(35) , 11843-54, (2005)] |
|
Switching of polymerization activity of cinnamoyl-alpha-cycl...
2009-04-21 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 7(8) , 1646-51, (2009)] |