| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
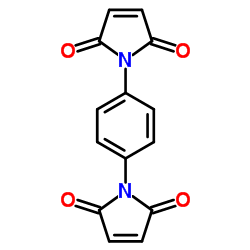 |
1,1'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis(1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione)
CAS:3278-31-7 |
|
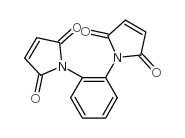 |
1H-Pyrrole-2,5-dione,1,1'-(1,2-phenylene)bis
CAS:13118-04-2 |