Palmitoylation modification of Galpha(o) depresses its susceptibility to GAP-43 activation.
Hui Yang, Lixin Wan, Fuchun Song, Mengxi Wang, Youguo Huang
Index: Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41(7) , 1495-501, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Interaction between GAP-43 (growth associated protein-43) and Galpha(o) (alpha subunit of Go protein) influences the signal transduction pathways leading to differentiation of neural cells. GAP-43 is known to increase guanine nucleotide exchange by Galpha(o), which is a major component of neuronal growth cone membranes. However, it is not clear whether GAP-43 stimulation is related to the Galpha(o) palmitoylation or the conversion of Galpha(o) from oligmers to monomers, which was shown to be a necessary regulatory factor in GDP/GTP exchange of Galpha(o). Here we expressed and purified GAP-43, GST-GAP-43 and Galpha(o) proteins, detected their stimulatory effect on [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding of Galpha(o). It was found that the EC(50) of both GAP-43 and GST-GAP-43 activation were tenfold lower in case of depalmitoylated Galpha(o) than palmitoylated Galpha(o). Non-denaturing gel electrophoresis and p-PDM cross-linking analysis revealed that addition of GST-GAP-43 induced disassociation of depalmitoylated Galpha(o) from oligomers to monomers, but did not influence the oligomeric state of palmitoylated Galpha(o), which suggests that palmitoylation is a key regulatory factor in GAP-43 stimulation on Galpha(o). These results indicated the interaction of GAP-43 and Galpha(o) could accelerate conversion of depalmitoylated Galpha(o) but not palmitoylated Galpha(o) from oligomers to monomers, so as to increase the GTPgammaS binding activity of Galpha(o). Results here provide new evidence about how signaling protein palmitoylation is involved in the G-protein-coupled signal transduction cascade, and give a useful clue on the participation of GAP-43 in G-protein cycle by its preferential activation of depalmitoylated Galpha(o).
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
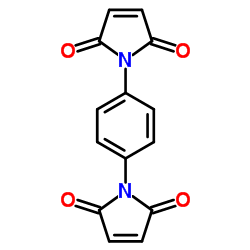 |
1,1'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis(1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione)
CAS:3278-31-7 |
C14H8N2O4 |
|
Helix packing in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli de...
1999-03-09 [Biochemistry 38(10) , 3120-6, (1999)] |
|
New aspects of the spontaneous polymerization of actin in th...
2009-04-10 [J. Mol. Biol. 387(4) , 869-82, (2009)] |
|
Probing the conformational states of the SH1-SH2 helix in my...
1998-11-24 [Biochemistry 37(47) , 16704-10, (1998)] |
|
Behavior of N-phenylmaleimide- and p-phenylenedimaleimide-re...
1998-10-05 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1367(1-3) , 127-33, (1998)] |
|
Kinetic investigation of the ligand dependence of rabbit ske...
1997-09-30 [Biochemistry 36(39) , 11952-8, (1997)] |