Changes in the thermal unfolding of p-phenylenedimaleimide-modified myosin subfragment 1 induced by its 'weak' binding to F-actin.
O V Kaspieva, O P Nikolaeva, V N Orlov, M A Ponomarev, V A Drachev, D I Levitsky
Index: FEBS Lett. 489(2-3) , 144-8, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to analyze the thermal unfolding of myosin subfragment 1 (S1) with the SH1 (Cys-707) and SH2 (Cys-697) groups cross-linked by N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide (pPDM-S1). It has been shown that F-actin affects the thermal unfolding of pPDM-S1 only at very low ionic strength, when some part of pPDM-S1 binds weakly to F-actin, but not at higher ionic strength (200 mM KCl). The weak binding of pPDM-S1 to F-actin shifted the thermal transition of pPDM-S1 by about 5 degrees C to a higher temperature. This actin-induced increase in thermal stability of pPDM-S1 was similar to that observed with 'strong' binding of unmodified S1 to F-actin. Our results show that actin-induced structural changes revealed by DSC in the myosin head occur not only upon strong binding but also on weak binding of the head to F-actin, thus suggesting that these changes may occur before the power-stroke and play an important role in the motor function of the head.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
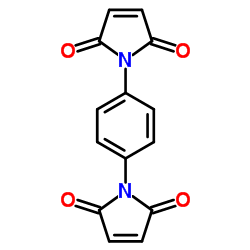 |
1,1'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis(1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione)
CAS:3278-31-7 |
C14H8N2O4 |
|
Helix packing in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli de...
1999-03-09 [Biochemistry 38(10) , 3120-6, (1999)] |
|
New aspects of the spontaneous polymerization of actin in th...
2009-04-10 [J. Mol. Biol. 387(4) , 869-82, (2009)] |
|
Probing the conformational states of the SH1-SH2 helix in my...
1998-11-24 [Biochemistry 37(47) , 16704-10, (1998)] |
|
Palmitoylation modification of Galpha(o) depresses its susce...
2009-07-01 [Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41(7) , 1495-501, (2009)] |
|
Behavior of N-phenylmaleimide- and p-phenylenedimaleimide-re...
1998-10-05 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1367(1-3) , 127-33, (1998)] |