| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
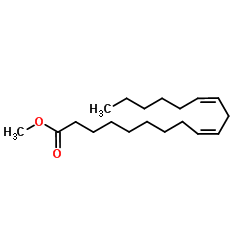 |
Methyl linoleate
CAS:112-63-0 |
|
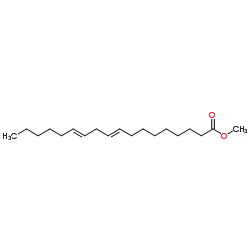 |
Methyl octadeca-9,12-dienoate
CAS:2566-97-4 |