Oxidation and dehalogenation of 4-chlorophenylacetate by a two-component enzyme system from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3.
A Markus, U Klages, S Krauss, F Lingens
Index: J. Bacteriol. 160(2) , 618-21, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In cell-free extracts from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 the conversion of 4-chlorophenylacetate to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate was demonstrated. By Sephacryl S-200 chromatography two protein fractions, A and B, were obtained which both were essential for enzyme activity. Fe2+ and NADH were cofactors of the reaction. NADPH also activated the enzyme, but less effectively than NADH. FAD had no influence on enzyme activity. 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate, 4-chloro-3-hydroxyphenylacetate, and 3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenylacetate were poor substrates for the enzyme, suggesting that these substances are not intermediates of the reaction. We therefore suggest that the reaction proceeds via a dioxygenated intermediate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
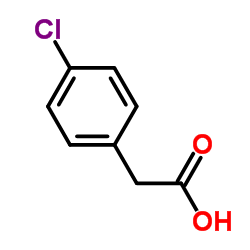 |
4-Chlorophenylacetic acid
CAS:1878-66-6 |
C8H7ClO2 |
|
Novel Chryseobacterium sp. PYR2 degrades various organochlor...
2015-09-15 [J. Environ. Manage. 161 , 350-7, (2015)] |
|
Degradation of 4-chlorophenylacetic acid by a Pseudomonas sp...
1981-04-01 [J. Bacteriol. 146(1) , 64-8, (1981)] |
|
Inhibition of estrogen-induced mammary tumor formation in MM...
2007-06-28 [Cancer Lett. 251(2) , 302-10, (2007)] |
|
Metabolomics reveals that aldose reductase activity due to A...
2015-07-01 [J. Viral Hepat. 22 , 617-24, (2015)] |
|
[Microbial degradation and 4-chlorophenylacetic acid. Chemic...
1982-04-01 [Hoppe. Seylers. Z. Physiol. Chem. 363(4) , 431-7, (1982)] |