| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
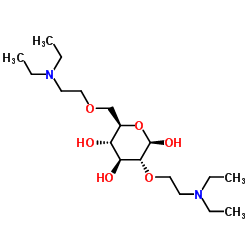 |
diethylaminoethyl cellulose
CAS:9013-34-7 |
|
 |
1,6-Hexanediamine
CAS:124-09-4 |
|
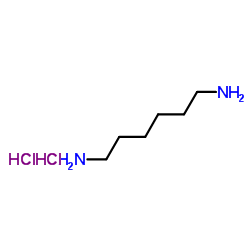 |
1,6-Hexanediamine dihydrochloride
CAS:6055-52-3 |