| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
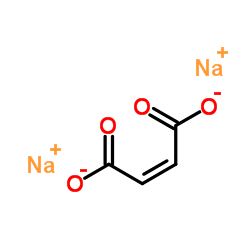 |
Disodium maleate
CAS:371-47-1 |
|
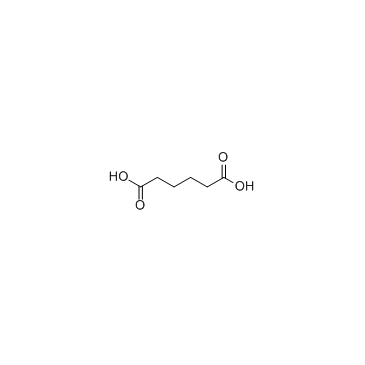 |
Adipic acid
CAS:124-04-9 |
|
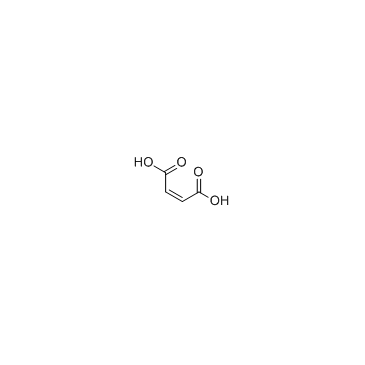 |
Maleic acid
CAS:110-16-7 |
|
 |
Poly(ethyl methacrylate)
CAS:9003-42-3 |
|
 |
poly(n-butyl methacrylate)
CAS:9003-63-8 |
|
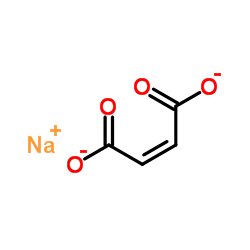 |
2-Butenedioate, (2Z)-, sodium salt (1:1)
CAS:3105-55-3 |