| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
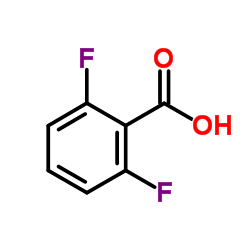 |
2,6-Difluorobenzoic acid
CAS:385-00-2 |
E Gattavecchia, A M Di Pietra, D Tonelli, A Borgatti
Index: J. Environ. Sci. Health B 16(2) , 159-66, (1981)
Full Text: HTML
Diflubenzuron (I) and its major degradation products 4-chlorophenyl urea (II), 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (III) and 4-chloroaniline (IV) were tested for their activity on Euglena gracilis Z. The inhibition on the growth and on the incorporation of glycine-U-14C in the protein of Euglena was measured in the presence of I-IV ranging 10 to 200 ppm. 4-chloroaniline caused a considerable inhibition at every tested level whereas I-III slightly affected only the incorporation. Therefore, it must be inferred that diflubenzuron shows no effect on growth and protein biosynthesis for this nontarget organism.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
2,6-Difluorobenzoic acid
CAS:385-00-2 |
C7H4F2O2 |
|
Synthesis of 2,6-difluoro-N-(3-[11C]methoxy-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-...
2013-02-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23(4) , 1017-21, (2013)] |
|
Synthesis and insecticidal evaluation of propesticides of be...
2005-01-12 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(1) , 38-41, (2005)] |
|
Metabolism of the insecticide teflubenzuron in rats.
1997-08-01 [Xenobiotica 27(8) , 801-17, (1997)] |
|
Structure of calcium 2,6-difluorobenzoate dihydrate.
1992-06-15 [Acta Crystallogr. C 48 ( Pt 6) , 1015-8, (1992)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2026 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved