| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
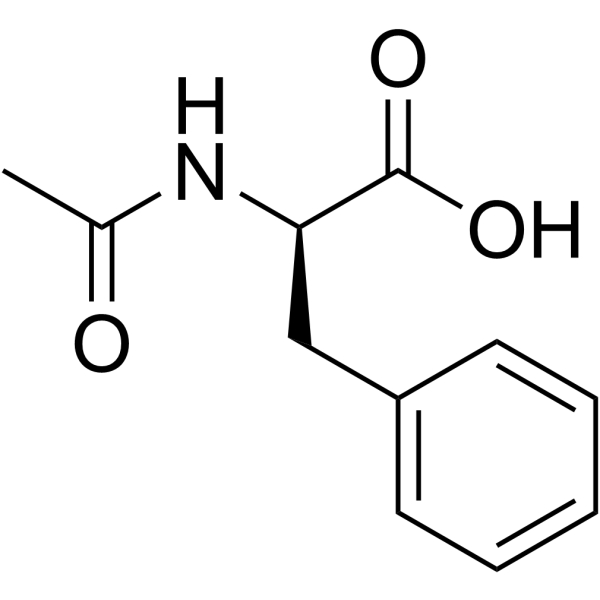 |
Ac-D-Phe-OH
CAS:10172-89-1 |
|
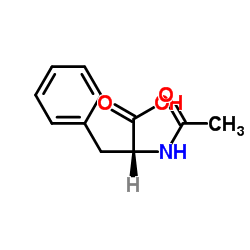 |
Ac-Phe-OH
CAS:2018-61-3 |