| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
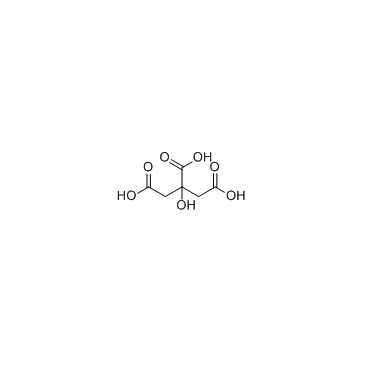 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
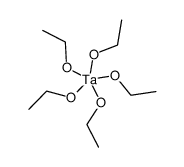 |
Tantalum(V) Ethoxide
CAS:6074-84-6 |
|
 |
UNII:TF4710DNP9
CAS:5094-24-6 |
|
 |
Sodium Hypophosphite
CAS:7681-53-0 |