Flavonoids and sesquiterpenes from Tecurium ramosissimum promote antiproliferation of human cancer cells and enhance antioxidant activity: a structure-activity relationship study.
Mohamed Ben Sghaier, Ines Skandrani, Nouha Nasr, Marie-Genviève Dijoux Franca, Leila Chekir-Ghedira, Kamel Ghedira
Index: Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 32(3) , 336-48, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Fractionation of the chloroformic extracts from Teucrium ramosissimum leaves resulted in the isolation of three flavonoids: genkwanin (1), cirsimaritin (2) and 4',7-dimethoxy apigenin (4) and one sesquiterpene: β-eudesmol (3). The structures were determined using data obtained from (1)H and (13)C NMR spectra, as well as by various correlation experiments (COSY, HMQC and HMBC). The antioxidant activities of the isolated flavonoids from T. ramosissimum leaves were evaluated by measuring their ability to scavenge the radical ABTS(+) and through chemical assays: cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC), reducing power (RP) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). Furthermore, the effects of T. ramosissimum isolated molecules, on inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human leukemia cells, were also examined. Cirsimaritin showed the best activity in the ABTS assay with TEAC value 2.04μM, whereas apigenin and 4',7-dimethoxy apigenin exhibited the highest antioxidant activity using the CUPRAC, RP and FRAP assays with TEAC values 10.5, 1.39 and 0.71μM respectively. The cytotoxic activity revealed that the β-eudesmol inhibited significantly the proliferation of K562 cells (IC(50)=20μg/ml).Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
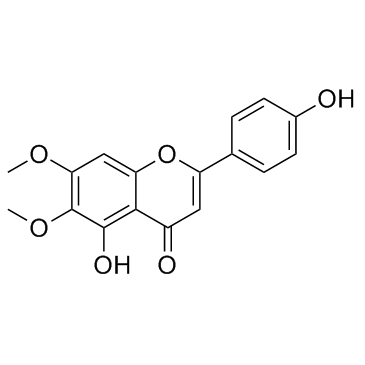 |
Scrophulein
CAS:6601-62-3 |
C17H14O6 |
|
[Studies on flavonoid constituents from herbs of Artemisia o...
2006-12-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 31(23) , 1959-61, (2006)] |
|
[Study on chemical constituents from Incarvillea arguta and ...
2005-09-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(17) , 1335-8, (2005)] |
|
[Determination of flavonoids in buds of Herba Artemisiae Sco...
2005-04-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(8) , 591-4, (2005)] |
|
Analysis of vervain flavonoids by HPLC/Diode array detector ...
1999-11-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(11) , 4579-82, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of [methyl-3H]diazepam binding to rat brain membr...
1994-09-01 [Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 15(5) , 385-8, (1994)] |