| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
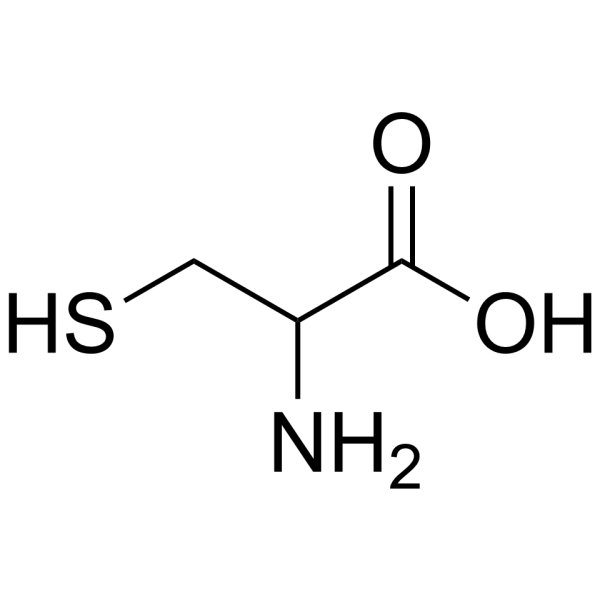 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
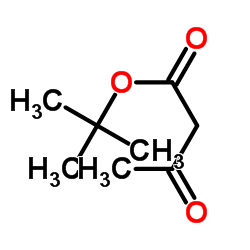 |
tert-Butyl acetoacetate
CAS:1694-31-1 |
|
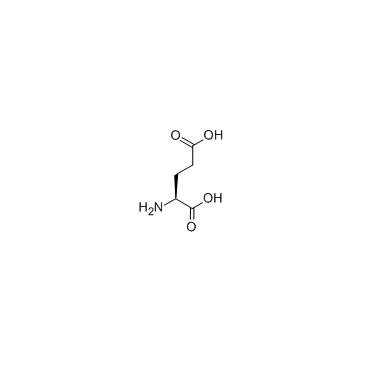 |
L-glutamic acid
CAS:56-86-0 |
|
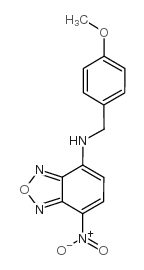 |
7-(4-Methoxybenzylamino)-4-nitrobenzoxadiazole
CAS:33984-50-8 |