| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
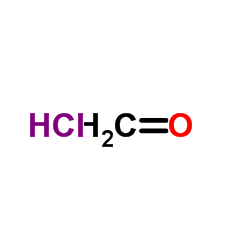 |
Formaldehyde hydrochloride (1:1)
CAS:1095-90-5 |
|
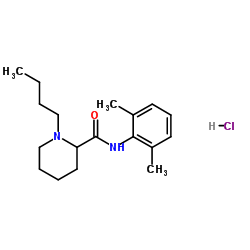 |
Bupivacaine hydrochloride
CAS:18010-40-7 |
|
 |
(+/-)-METHADONE
CAS:76-99-3 |