Radical-derived oxidation products of 5-aminosalicylic acid and N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid.
C Fischer, U Klotz
Index: J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 661(1) , 57-68, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
5-Aminosalicylic acid is an agent effective in the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Its ability to scavenge radicals is considered to be a major factor responsible for its therapeutic efficacy. In this study oxidation products of aminosalicylates with hydroxyl radicals were produced. The compounds that could be discovered by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis originate from a 1,4-benzoquinone monoimine intermediate which subsequently undergoes multiple reactions such as hydrolysis, reductive 1,4-Michael addition, reoxidation and decarboxylation. Some of these products could represent metabolites formed under in vivo conditions and thus provide a tool for screening biological material from subjects under different clinical conditions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
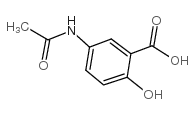 |
N-Acetyl Mesalazine
CAS:51-59-2 |
C9H9NO4 |
|
Simultaneous determination of 5-aminosalicylic acid, acetyl-...
1995-12-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 14(1-2) , 175-80, (1995)] |
|
Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of balsalazide in ped...
2009-11-01 [J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49(5) , 571-9, (2009)] |
|
Superoxide inhibition following different stimuli of respira...
1994-01-01 [Dig. Dis. Sci. 39(1) , 145-51, (1994)] |
|
Pharmacokinetic studies of benzalazine.
1994-12-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 44(12) , 1381-3, (1994)] |
|
Inhibitory effect of flavonoids on the efflux of N-acetyl 5-...
2009-01-01 [J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009 , 467489, (2009)] |