| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
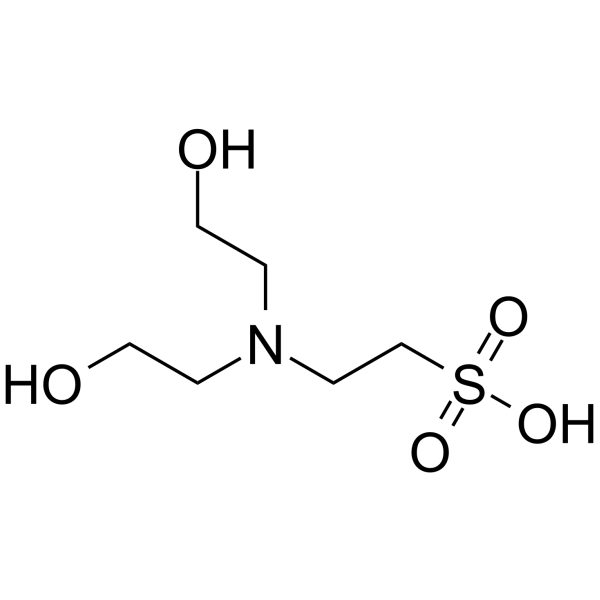 |
BES
CAS:10191-18-1 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
HEPES sodium salt
CAS:75277-39-3 |
|
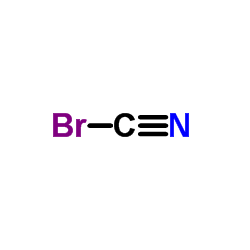 |
Cyanogen bromide
CAS:506-68-3 |