Anti-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity of 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol.
Eun-Ju Lim, Hyun-Jung Kang, Hyun-Joo Jung, Eun-Hee Park
Index: J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 59(9) , 1235-40, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol (HBA), one of the well-known phenolic compounds in diverse plants, displayed a significant inhibition in the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) angiogenesis assay. HBA was shown to contain an anti-inflammatory activity in carrageenan-induced air pouch model in rats and acetic acid-induced permeability model in mice. Anti-nociceptive activity of HBA was also assessed using the acetic acid-induced writhing test in mice. HBA was able to suppress production of nitric oxide (NO) and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW264.7 macrophages. In the macrophages, the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was diminished by HBA. Taken together, HBA possesses anti-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity possibly via its down-regulating activity on NO production, which may be partly responsible for the pharmacological efficacy of several folkloric medicines.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
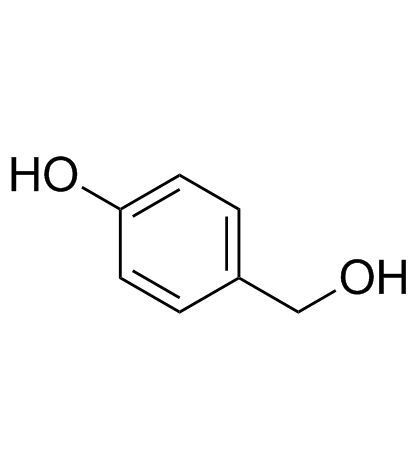 |
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
CAS:623-05-2 |
C7H8O2 |
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of str...
2009-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009)] |
|
High tolerance and physiological mechanism of Zymomonas mobi...
2015-09-01 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112 , 1770-82, (2015)] |
|
Predicting the substrate specificity of a glycosyltransferas...
2011-01-01 [FEBS J. 278(2) , 390-400, (2011)] |
|
Inhibition of GABA shunt enzymes' activity by 4-hydroxybenza...
2006-02-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16 , 592-5, (2006)] |
|
A cascade biodegradable polymer based on alternating cycliza...
2009-12-30 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(51) , 18327-34, (2009)] |