| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Caffeine
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
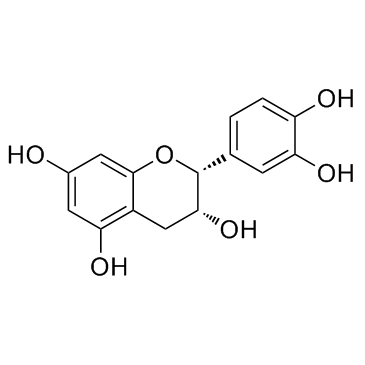 |
Epicatechin
CAS:490-46-0 |
|
 |
CHLOROPHYLL A
CAS:479-61-8 |
|
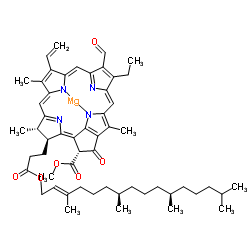 |
b-Chlorophyll
CAS:519-62-0 |
|
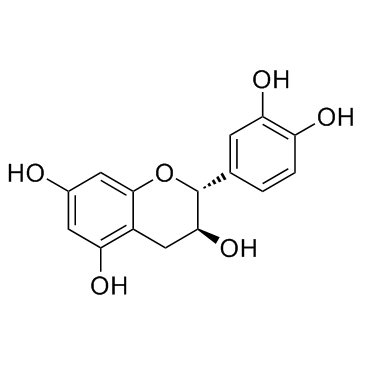 |
Catechin
CAS:154-23-4 |
|
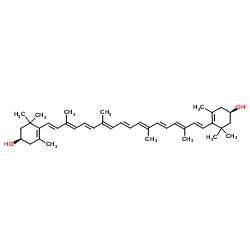 |
Zeaxanthin
CAS:144-68-3 |