The site of antiviral action of 3-nitrosobenzamide on the infectivity process of human immunodeficiency virus in human lymphocytes.
W G Rice, C A Schaeffer, L Graham, M Bu, J S McDougal, S L Orloff, F Villinger, M Young, S Oroszlan, M R Fesen
Index: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90 , 9721, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The C-nitroso compound 3-nitrosobenzamide, which has been shown to remove zinc from the retroviral-type zinc finger of p7NC nucleocapsid proteins, inhibits acute infection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in cultured human lymphocytes. The attachment of the virus to lymphocytes and the activities of critical viral enzymes, such as reverse transcriptase, protease, and integrase, are not affected by 3-nitrosobenzamide. However, the process of reverse transcription to form proviral DNA is effectively abolished by the drug, identifying the mode of action of 3-nitrosobenzamide as interrupting the role of p7NC in accurate proviral DNA synthesis during the infectious phase of the virus life cycle.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
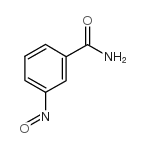 |
3-nitrosobenzamide
CAS:144189-66-2 |
C7H6N2O2 |
|
Inhibition of the replication of native and 3'-azido-2',3'-d...
1993-07-12 [FEBS Lett. 326 , 140, (1993)] |
|
Structure/function correlations among coupled binuclear copp...
2012-07-03 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109(27) , 10793-7, (2012)] |
|
A copper-containing oxidase catalyzes C-nitrosation in nitro...
2010-09-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 6(9) , 641-3, (2010)] |
|
Anti-HIV agents that selectively target retroviral nucleocap...
1998-04-23 [J. Med. Chem. 41(9) , 1371-81, (1998)] |
|
Inhibition of HIV-1 infectivity by zinc-ejecting aromatic C-...
1993-02-04 [Nature 361 , 473, (1993)] |