| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
NAD+
CAS:53-84-9 |
|
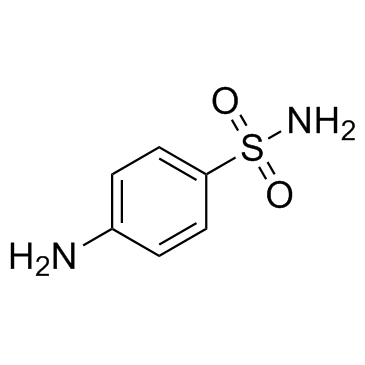 |
Sulfanilamide
CAS:63-74-1 |
|
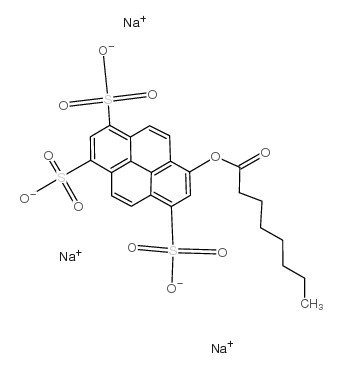 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |
|
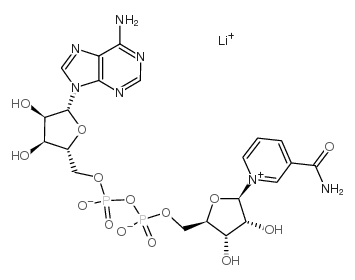 |
NAD+ lithium
CAS:64417-72-7 |
|
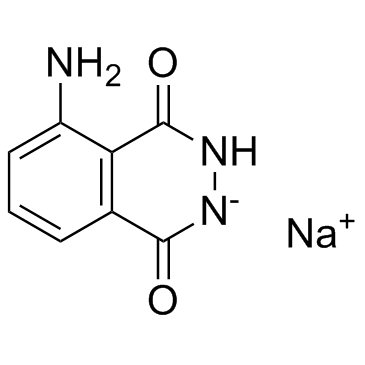 |
LUMINOL SODIUM SALT
CAS:20666-12-0 |