Isolation and characterization of a new bacterium capable of biotransforming cis -epoxysuccinic acid to D(-) -tartaric acid.
Xia Li, Xiaohang Ma, Yuhua Zhao, Xiaoming Jia, Lei Kai, Kangping Guo, Weifeng Zhao
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 267(2) , 214-20, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A bacterial strain 1-3 capable of enantioselectively hydrolyzing cis-epoxysuccinic acid to D(-)-tartaric acid was isolated from soil. Phenotypic characteristics, Biolog GN test and phylogenetic analysis of strain 1-3 indicated that it belongs to the genus Bordetella. cis-Epoxysuccinic acid could be used as a carbon source and inducer for production of cis-epoxysuccinic acid hydrolase. After the purification of the enzymatic biotransformed product, a colorless and scentless crystal was obtained, which was confirmed to be the tartaric acid with laevorotatory optical rotation by the (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and optical rotation analysis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
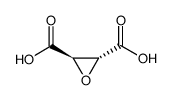 |
(+/-)-THIOPENTALSODIUMSALT/SODIUMCARBONATE
CAS:141-36-6 |
C4H4O5 |
|
Inhibitory function of p21Cip1/WAF1 in differentiation of pr...
1998-05-15 [Science 280(5366) , 1069-72, (1998)] |
|
[Extraction of Pb from sewage sludge with PESA].
2008-01-01 [Huan Jing Ke Xue 29(1) , 158-63, (2008)] |
|
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abund...
1995-08-04 [Science 269(5224) , 682-5, (1995)] |
|
Flow calorimetry--a useful tool for determination of immobil...
2004-02-01 [Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 32(1) , 77-89, (2004)] |
|
Enzymatic formation of ether linkage producing shoyuflavones...
2000-06-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(6) , 2149-54, (2000)] |