Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27.
M Pagano, S W Tam, A M Theodoras, P Beer-Romero, G Del Sal, V Chau, P R Yew, G F Draetta, M Rolfe
Index: Science 269(5224) , 682-5, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The p27 mammalian cell cycle protein is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Both in vivo and in vitro, p27 was found to be degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. The human ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes Ubc2 and Ubc3 were specifically involved in the ubiquitination of p27. Compared with proliferating cells, quiescent cells exhibited a smaller amount of p27 ubiquitinating activity, which accounted for the marked increase of p27 half-life measured in these cells. Thus, the abundance of p27 in cells is regulated by degradation. The specific proteolysis of p27 may represent a mechanism for regulating the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
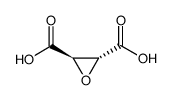 |
(+/-)-THIOPENTALSODIUMSALT/SODIUMCARBONATE
CAS:141-36-6 |
C4H4O5 |
|
Inhibitory function of p21Cip1/WAF1 in differentiation of pr...
1998-05-15 [Science 280(5366) , 1069-72, (1998)] |
|
[Extraction of Pb from sewage sludge with PESA].
2008-01-01 [Huan Jing Ke Xue 29(1) , 158-63, (2008)] |
|
Flow calorimetry--a useful tool for determination of immobil...
2004-02-01 [Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 32(1) , 77-89, (2004)] |
|
Enzymatic formation of ether linkage producing shoyuflavones...
2000-06-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(6) , 2149-54, (2000)] |
|
Isolation and characterization of a new bacterium capable of...
2007-02-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 267(2) , 214-20, (2007)] |