| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
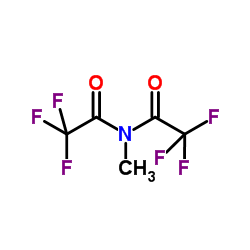 |
N-Methyl-bis(trifluoroacetamide)
CAS:685-27-8 |
|
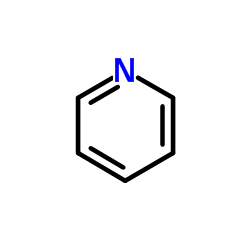 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |
|
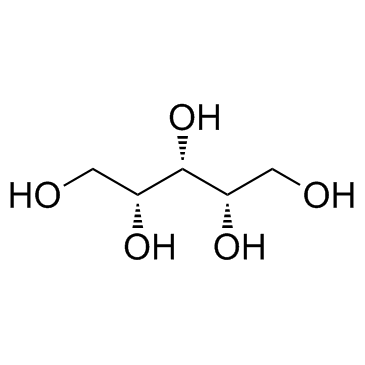 |
Xylitol
CAS:87-99-0 |
|
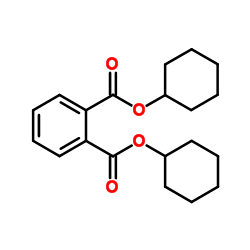 |
Dicyclohexyl phthalate
CAS:84-61-7 |
|
 |
Tryptophol
CAS:526-55-6 |
|
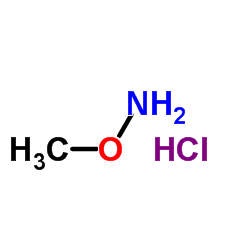 |
O-Methoxyamine HCl
CAS:593-56-6 |