| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
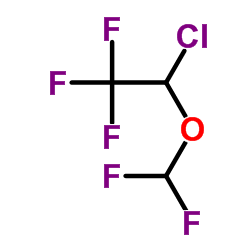 |
Isoflurane
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
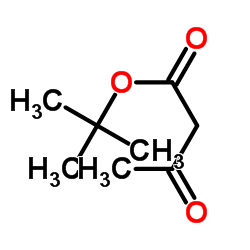 |
tert-Butyl acetoacetate
CAS:1694-31-1 |
|
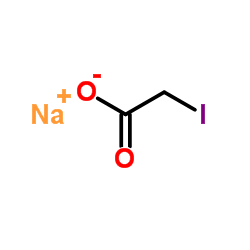 |
sodiumiodoacetate
CAS:305-53-3 |