Degradation of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate by Pseudomonas sp. BN9.
A Stolz, H J Knackmuss
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 108(2) , 219-24, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The aerobic degradation of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate by Pseudomonas sp. BN9 was studied. Intact cells of Pseudomonas sp. BN9 grown with 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate oxidized 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate but not salicylate. Cell-free extracts of Pseudomonas sp. BN9 converted 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate after the addition of NAD(P)H. A partially purified protein fraction converted 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate with NADH to 1,2,4-trihydroxybenzene. 1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene was converted by a 1,2-dioxygenase to maleylpyruvate, which was reduced by a NADH-dependent enzyme to 3-oxoadipate. 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoate 1-monooxygenase, 1,2,4-trihydroxybenzene 1,2-dioxygenase and maleylpyruvate reductase were induced in Pseudomonas sp. BN9 after growth with 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
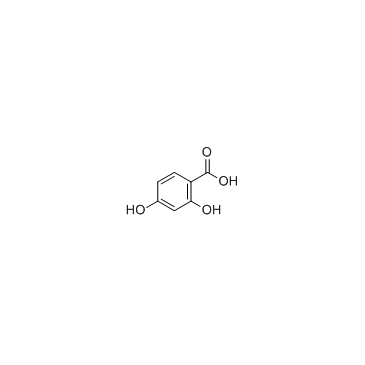 |
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:89-86-1 |
C7H6O4 |
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a ...
2011-01-27 [J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011)] |
|
Application of Electrochemiluminescence for the Evaluation o...
2015-01-01 [Anal. Sci. 31 , 629-34, (2015)] |
|
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzaldehyde thiose...
2007-03-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 2006-15, (2007)] |
|
Inhibition of 15-lipoxygenase-catalysed oxygenation of arach...
2008-04-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 4589-93, (2008)] |
|
Application of capillary electrophoresis with electrokinetic...
2015-09-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 7093-100, (2015)] |