| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
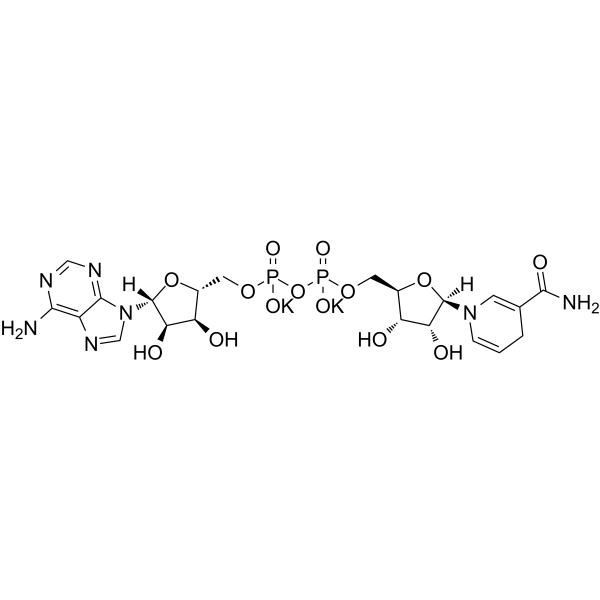 |
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced dipotassium
CAS:104809-32-7 |
|
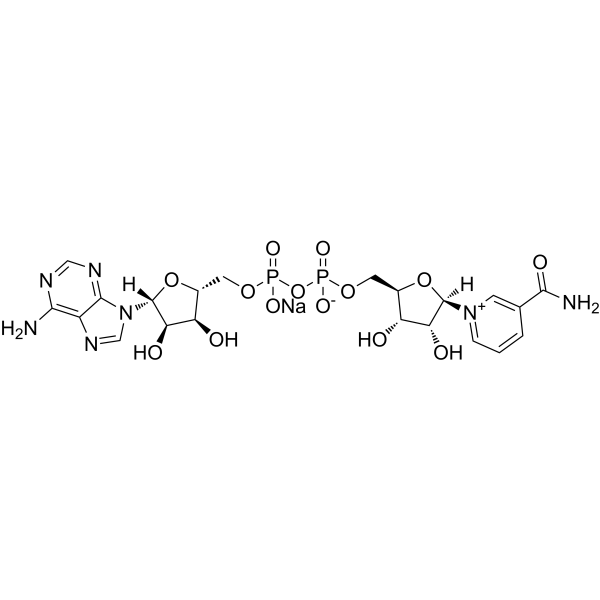 |
NAD sodium
CAS:20111-18-6 |
|
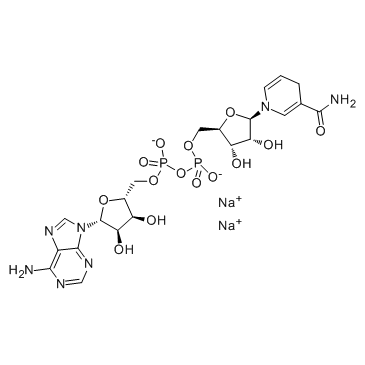 |
NADH disodium salt
CAS:606-68-8 |
|
 |
NAD+
CAS:53-84-9 |
|
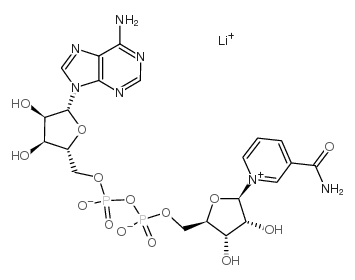 |
NAD+ lithium
CAS:64417-72-7 |