Heat resistance of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple juice.
D F Splittstoesser, M R McLellan, J J Churey
Index: J. Food Prot. 59(3) , 226-9, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The objective was to determine the effect of cider composition on the heat resistance of Escherichia coli O157:H7. The average D52 value in a model Empire apple juice was 18 min with a z value of 4.8 degrees C. Increasing the Brix from 11.8 to 16.5 degrees had no effect on thermal resistance, while increasing L-malic acid from 0.2 to 0.8%, or reducing the pH from 4.4 to 3.6 sensitized the cells to heat. The greatest effect on heat resistance was afforded by the preservatives benzoic and sorbic acids: D50 values in ciders containing 1,000 mg/l were 5.2 min in the presence of sorbic acid and only 0.64 min in the presence of benzoic acid. Commercial apple juice concentrates yielded lower numbers of survivors than single-strength juices even though their higher sugar concentrations of about 46 degrees Brix increased heat resistance.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
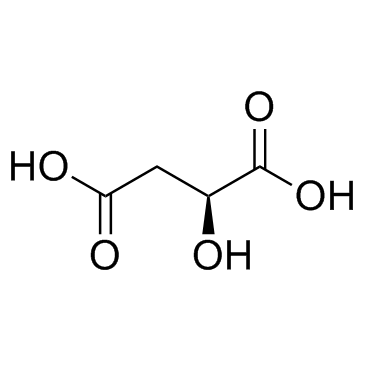 |
L-(-)-Malic acid
CAS:97-67-6 |
C4H6O5 |
|
Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrosp...
1993-01-01 [J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 16(4) , 648-69, (1993)] |
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a ...
1994-06-01 [Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994)] |
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine ...
2009-02-12 [Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009)] |
|
Automated screening of urine samples for carbohydrates, orga...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 562(1-2) , 125-38, (1991)] |
|
Quantitative analysis for organic acids in biological sample...
1989-04-01 [Clin. Chem. 35(4) , 587-95, (1989)] |