| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
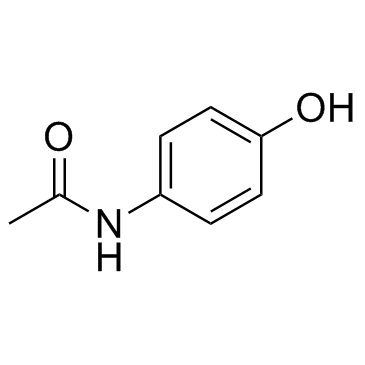 |
4-Acetamidophenol
CAS:103-90-2 |
|
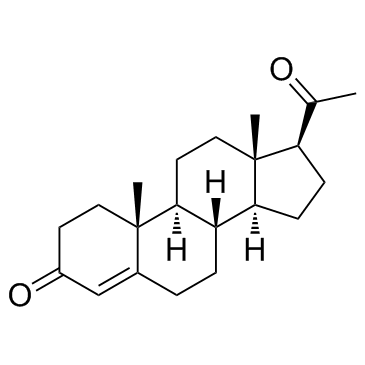 |
Progesterone
CAS:57-83-0 |
|
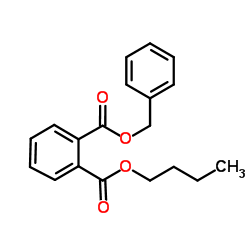 |
Benzyl butyl phthalate
CAS:85-68-7 |
|
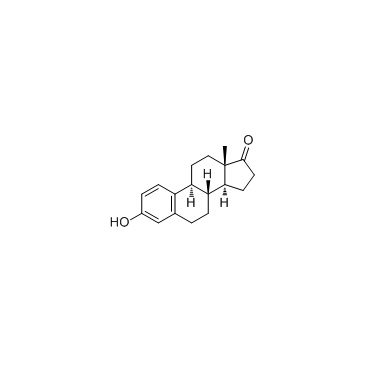 |
Estrone
CAS:53-16-7 |
|
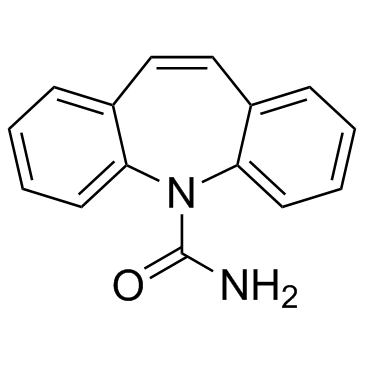 |
Carbamazepine
CAS:298-46-4 |
|
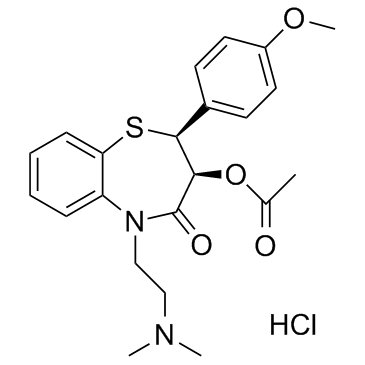 |
diltiazem hydrochloride
CAS:33286-22-5 |