| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
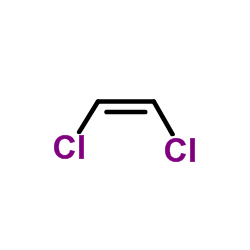 |
(Z)-1,2-Dichloroethene
CAS:156-59-2 |
|
 |
(E)-1,2-Dichloroethene
CAS:156-60-5 |
|
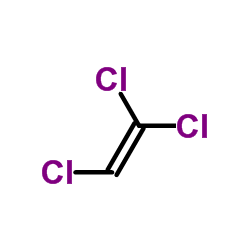 |
Trichloroethylene
CAS:79-01-6 |
|
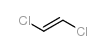 |
1,2-dichloroethylene
CAS:540-59-0 |