Columbin inhibits cholesterol uptake in bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei-A possible trypanocidal mechanism.
A J Nok, B A Sallau, E Onyike, N M Useh
Index: J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 20(4) , 365-8, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The diterpenoid furanolactone (columbin) from Aristolochia albida inhibited growth of culture forms of Trypanosoma brucei. In vitro analysis of the compound at 5-250 microg/ml showed complete lysis of the parasites within 10-20 minutes post incubation. At 50 microg/ml, columbin killed about 50% of the parasites which initially appeared swollen under phase contrast microscopy. Also the total amount of cholesterol diminished dose-dependently in the presence of 10-100 microg/ml of columbin after a 3-day incubation period. In vivo analysis of the compound in T. brucei-infected mice revealed that 25 mg/kg administered for 3 consecutive days, completely cleared the parasites from the peripheral circulation. However, columbin could not clear parasites in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
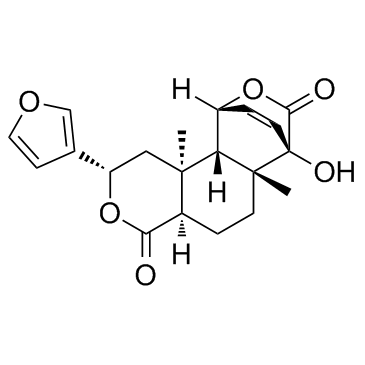 |
Columbin
CAS:546-97-4 |
C20H22O6 |
|
In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of columbi...
2012-03-05 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 678(1-3) , 61-70, (2012)] |
|
A bitter diterpenoid furanolactone columbin from Calumbae Ra...
2002-09-26 [Cancer Lett. 183(2) , 131-9, (2002)] |
|
Inhibition of Naja nigricolis venom acidic phospholipase A2 ...
2002-02-01 [J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 17(1) , 55-9, (2002)] |
|
Columbin isolated from calumbae radix affects the sleeping t...
1995-04-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18(4) , 634-6, (1995)] |
|
Quantitative LC/MS/MS method and pharmacokinetic studies of ...
2007-06-01 [Biomed. Chromatogr. 21(6) , 642-8, (2007)] |