Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters
2006-04-01
Inhibition of intercellular junctional communication in human fibroblasts by triphenylmethane, triphenylmethylchloride, tetraphenylboron and related compounds.
Maura Lodovici, Stefano Menichetti, Caterina Viglianisi, Silvia Caldini, Elisa Giuliani
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 847(1) , 1-7, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hydroxylated 4-thiaflavans, possessing the antioxidant features of catechol containing flavonoids and/or tocopherols, were evaluated as protective agents against oxidation damage induced in herring sperm DNA by cumene hydroperoxide (CumOOH) or by the glutathione/ferric ion (GSH/Fe(3+)) system. Our data indicate that the effective protection exerted by some of the tested compounds is overall higher than those provided by catechin and alpha-tocopherol, which might be attributed both to the scavenging properties and chelation of Fe(2+) ions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
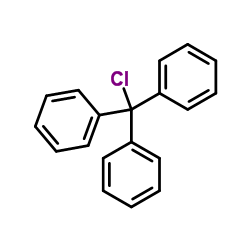 |
Triphenylmethyl Chloride
CAS:76-83-5 |
C19H15Cl |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Structure-activity relationship of S-trityl-L-cysteine analo...
2008-03-13 [J. Med. Chem. 51 , 1115-25, (2008)] |
|
Thermally robust and porous noncovalent organic framework wi...
2014-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 5 , 5131, (2014)] |
|
Comparative susceptibility of newborn and young rats to six ...
2005-12-01 [Congenit. Anom. (Kyoto.) 45(4) , 137-45, (2005)] |
|
Method for activation and recycling of trityl resins.
2012-08-17 [J. Org. Chem. 77(16) , 7071-5, (2012)] |
|
Pediatric susceptibility to 18 industrial chemicals: a compa...
2007-04-01 [Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 47(3) , 296-307, (2007)] |