| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
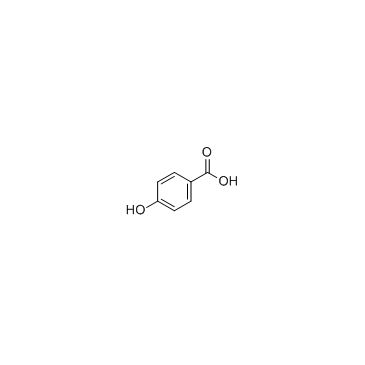 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:99-96-7 |
|
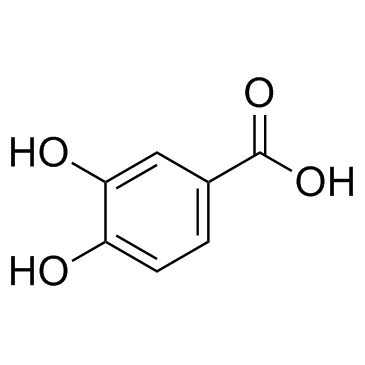 |
protocatechuic acid
CAS:99-50-3 |
|
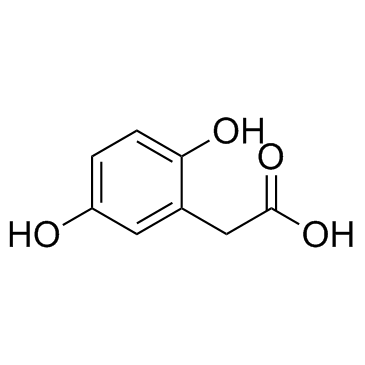 |
HOMOGENTISIC ACID
CAS:451-13-8 |
|
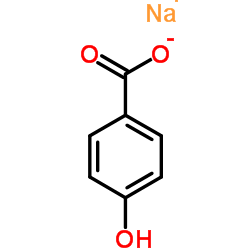 |
Sodium 4-hydroxybenzoate
CAS:114-63-6 |