| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
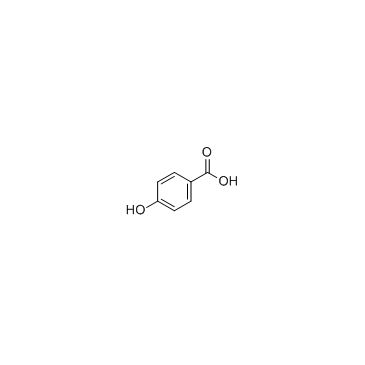 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:99-96-7 |
|
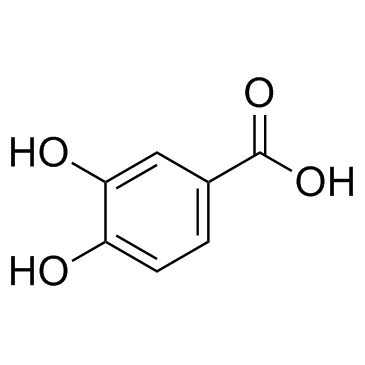 |
protocatechuic acid
CAS:99-50-3 |
|
 |
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate
CAS:7782-63-0 |
|
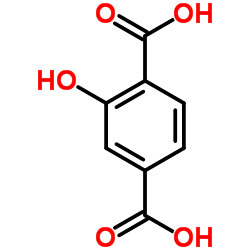 |
2-Hydroxyterephthalic acid
CAS:636-94-2 |
|
 |
Terephthalic acid
CAS:100-21-0 |