| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
![Sodium [(4-aminobenzoyl)amino]acetate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/164/94-16-6.png) |
Sodium [(4-aminobenzoyl)amino]acetate
CAS:94-16-6 |
|
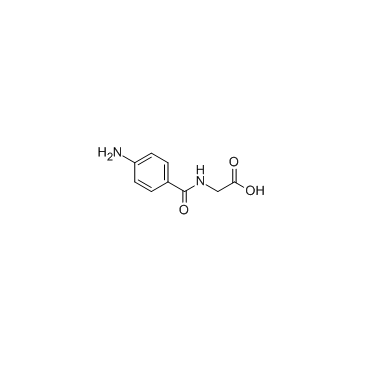 |
4-Aminohippuric acid
CAS:61-78-9 |