| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
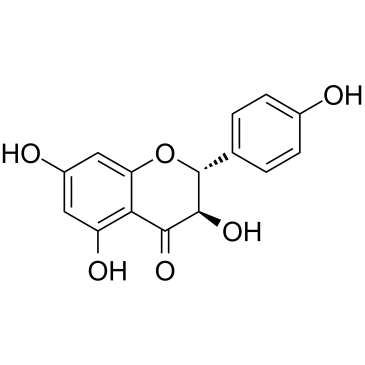 |
Aromadendrin
CAS:480-20-6 |
|
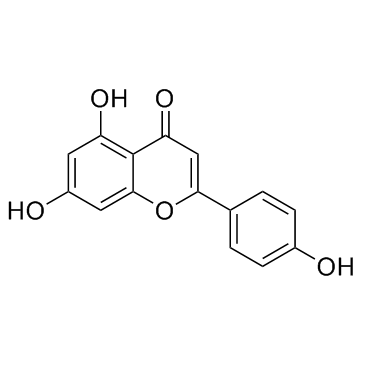 |
Apigenin
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
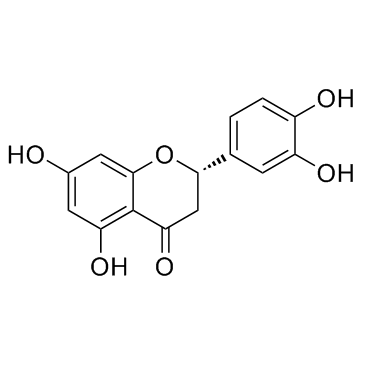 |
Eriodictyol
CAS:552-58-9 |
|
 |
(±)-Naringenin
CAS:67604-48-2 |
|
 |
Kaempferol
CAS:520-18-3 |