| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
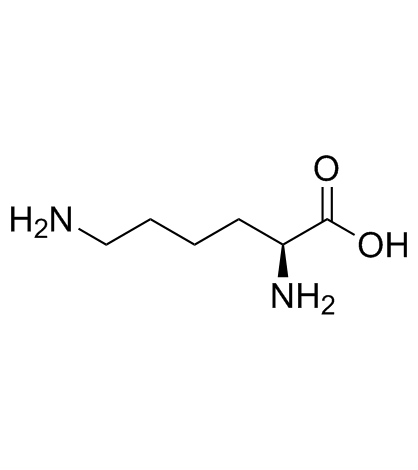 |
L-Lysine
CAS:56-87-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
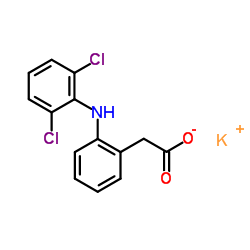 |
Diclofenac potassium
CAS:15307-81-0 |
|
 |
ketoprofen
CAS:22071-15-4 |
|
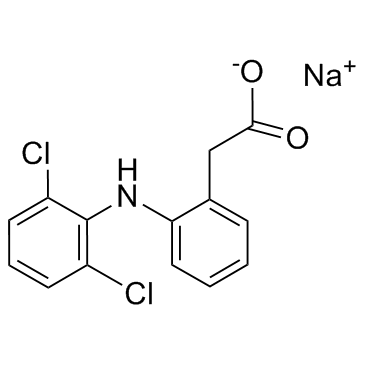 |
Diclofenac sodium
CAS:15307-79-6 |
|
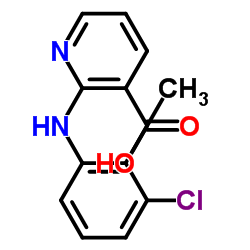 |
clonixin
CAS:17737-65-4 |
|
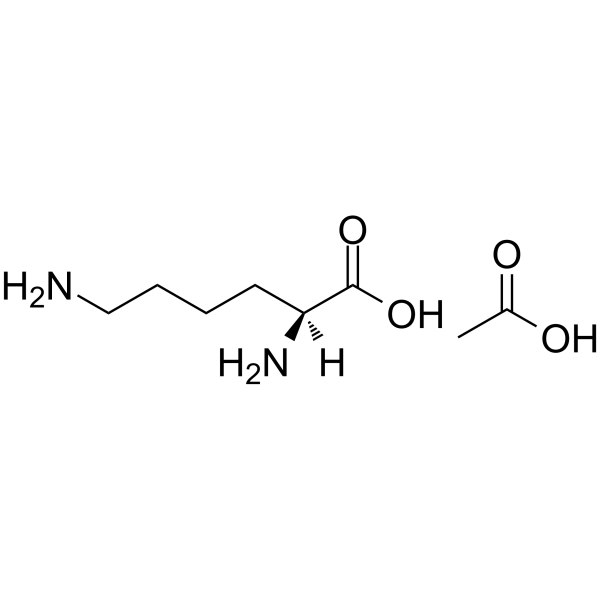 |
L-Lysine monoacetate
CAS:57282-49-2 |