| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
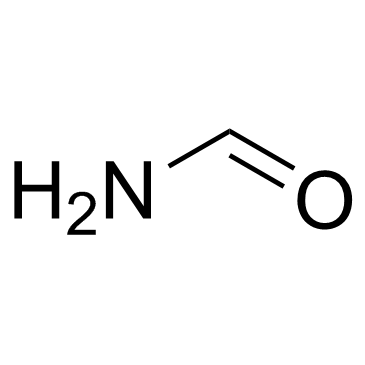 |
Formamide
CAS:75-12-7 |
|
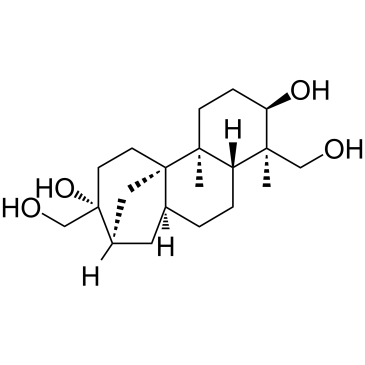 |
(+)-Aphidicolin
CAS:38966-21-1 |
|
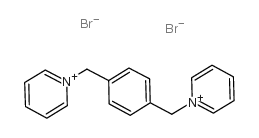 |
dpx
CAS:14208-10-7 |
|
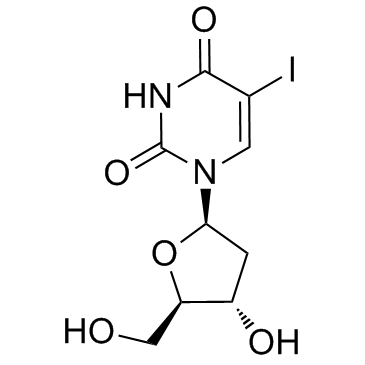 |
idoxuridine
CAS:54-42-2 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
3-Amino-9-ethylcarbazole
CAS:132-32-1 |