| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
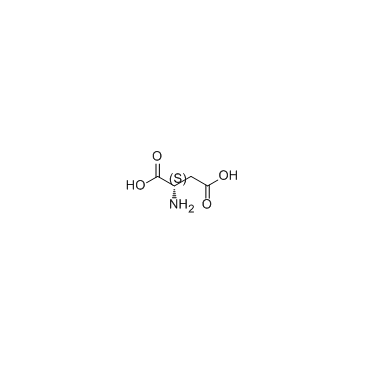 |
L-Aspartic acid
CAS:56-84-8 |
|
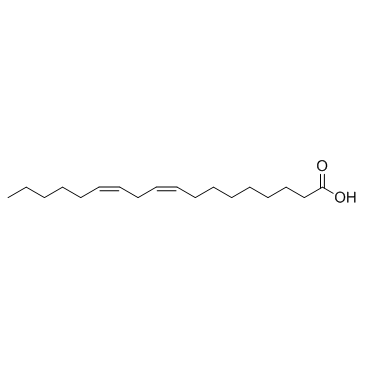 |
Linoleic acid
CAS:60-33-3 |
|
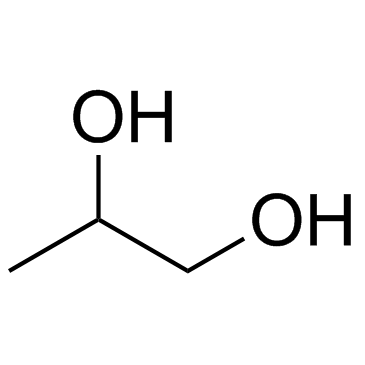 |
Propylene Glycol
CAS:57-55-6 |
|
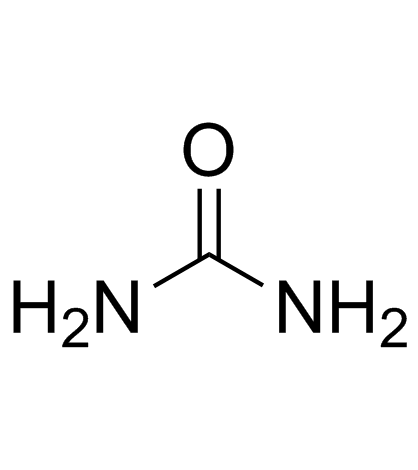 |
Urea
CAS:57-13-6 |
|
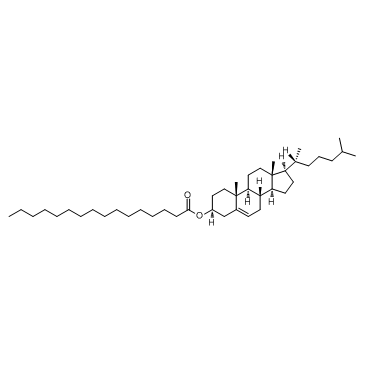 |
cholesteryl palmitate
CAS:601-34-3 |
|
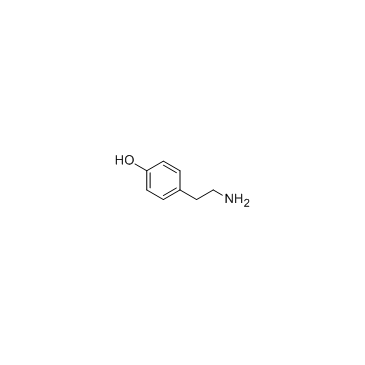 |
Tyramine
CAS:51-67-2 |
|
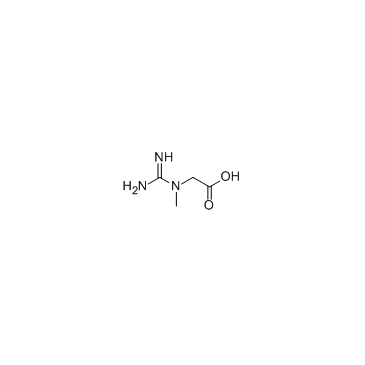 |
Creatine
CAS:57-00-1 |
|
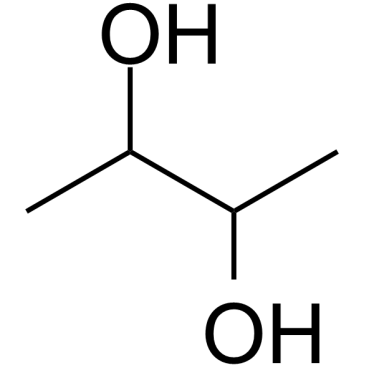 |
(2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-Butanediol
CAS:513-85-9 |