| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
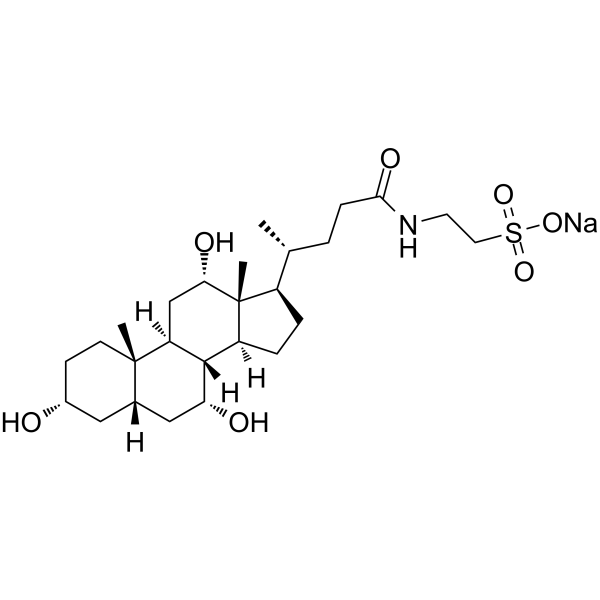 |
Sodium taurocholate
CAS:145-42-6 |
|
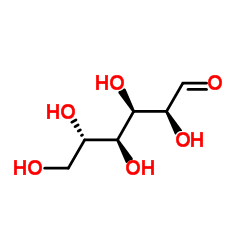 |
L-Glucose
CAS:921-60-8 |
|
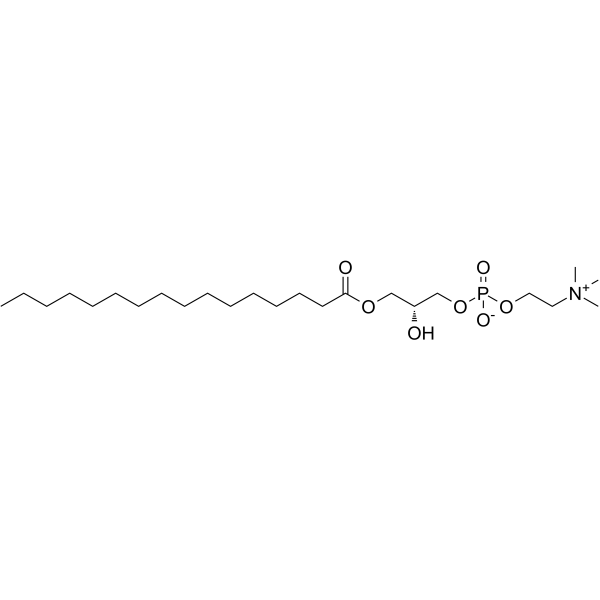 |
1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
CAS:17364-16-8 |