| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
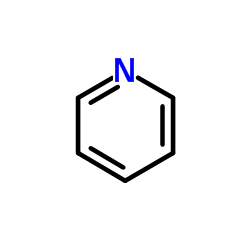 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |
|
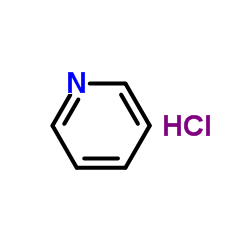 |
Pyridine chlorhydrate
CAS:628-13-7 |
|
 |
Pyridine hydrobromide
CAS:18820-82-1 |
|
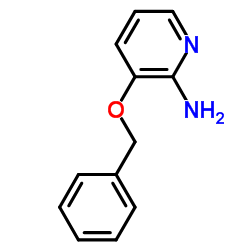 |
2-Amino-3-benzyloxypyridine
CAS:24016-03-3 |