Safety and efficacy of antioxidants-loaded nanoparticles for an anti-aging application.
Cândice C Felippi, Dileusa Oliveira, Alessandra Ströher, Anderson R Carvalho, Eliana A M Aquino Van Etten, Márcia Bruschi, Renata P Raffin
Index: J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 8(2) , 316-21, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The aim of this work was to perform a pilot study on the safety and efficacy of nanoparticle formulation for cosmetic application. The encapsulated actives in the nanoparticles were a blend of coenzyme Q10, retinyl palmitate, tocopheryl acetate, grape seed oil and linseed oil. The nanoparticle suspension was characterized in terms of pH and particle size. For the safety assessment, alternative methods as cytotoxicity and HET CAM were used. The clinical skin compatibility tests were also performed. The efficacy was evaluated in healthy volunteers presenting different degrees of periorbital wrinkles. Skin hydration was performed by corneometry. The nanoparticles presented narrow size around 140 nm and pH close to neutral and were suitable to cutaneous application. The alternative tests demonstrated that the nanoparticles did not present potential to induce skin irritant effects, cytotoxicity or generate oxidative stress. The clinical assays confirmed the in vitro results, demonstrating the safety of the nanoparticles, which were not irritant, sensitizing and comedogenic. Furthermore, the exposure to UVA light did not cause photoxicity. Regarding the efficacy, nanoparticles presented significant reduction in wrinkle degree after 21 days of application compared to the control. The volunteers could differentiate the nanoparticles and the control product by means of subjective analyses. In conclusion, the nanoparticles containing antioxidant actives were safe for topical use and presented anti-aging activity in vivo and are suitable to be used as cosmetic ingredient.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
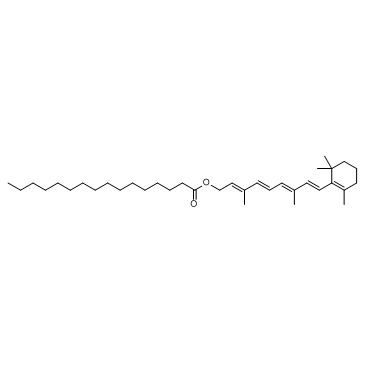 |
Retinyl palmitate
CAS:79-81-2 |
C36H60O2 |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the predicti...
2010-07-19 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010)] |
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-indu...
2010-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010)] |
|
Lack of Impact of High Dietary Vitamin A on T Helper 2-Depen...
2015-01-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1827-30, (2015)] |
|
Retinylamine Benefits Early Diabetic Retinopathy in Mice.
2015-08-28 [J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 21568-79, (2015)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of 13-cis and all-trans vitamin A...
2013-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 96(5) , 1073-81, (2013)] |