| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
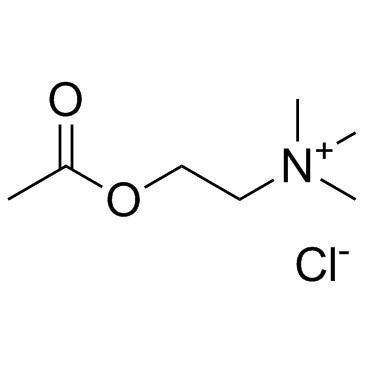 |
Acetylcholine chloride
CAS:60-31-1 |
|
 |
Serotonin hydrochloride
CAS:153-98-0 |
|
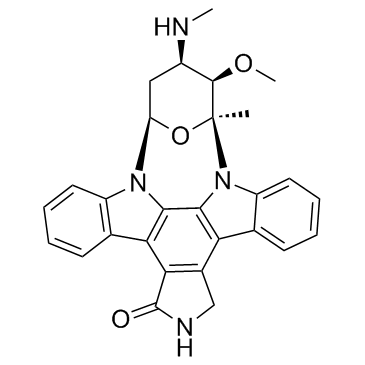 |
Staurosporine
CAS:62996-74-1 |
|
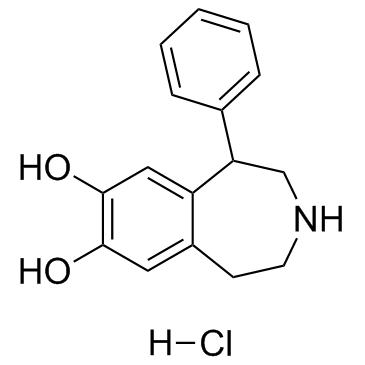 |
SKF38393 HCl
CAS:62717-42-4 |
|
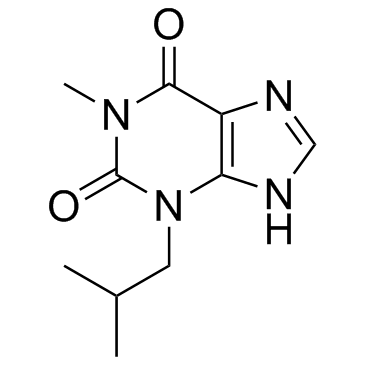 |
3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine
CAS:28822-58-4 |
|
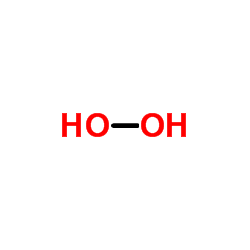 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
4-Aminobutanoic acid
CAS:56-12-2 |
|
 |
RO 20-1724
CAS:29925-17-5 |
|
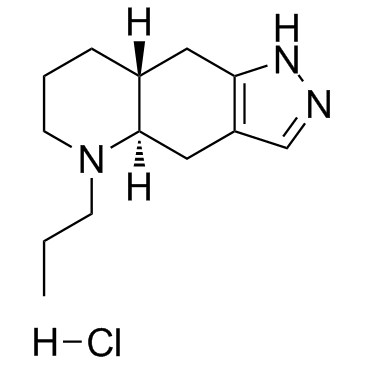 |
(-)-Quinpirole hydrochloride
CAS:85798-08-9 |