| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
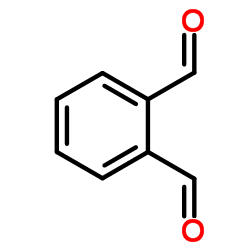 |
o-Phthalaldehyde
CAS:643-79-8 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-pNA
CAS:70967-97-4 |
|
 |
Ramipril
CAS:87333-19-5 |
|
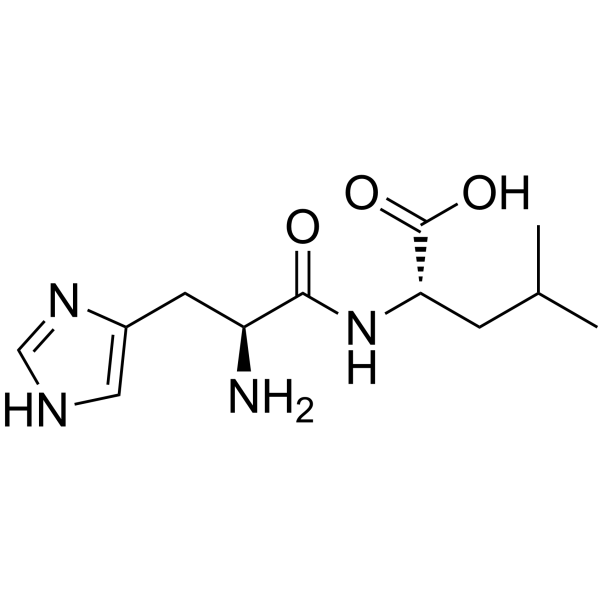 |
H-His-Leu-OH
CAS:7763-65-7 |