A new quinolone and other constituents from the fruits of Tetradium ruticarpum: effects on neutrophil pro-inflammatory responses.
Tzu-Ying Wang, Jin-Bin Wu, Tsong-Long Hwang, Yueh-Hsiung Kuo, Jih-Jung Chen
Index: Chem. Biodivers. 7(7) , 1828-34, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The fruit of Tetradium ruticarpum is widely used in healthcare products for the improvement of blood circulation, headache, abdominal pain, amenorrhea, chill limbs, migraine, and nausea. A new quinolone, 2-[(6Z,9Z)-pentadeca-6,9-dienyl]quinolin-4(1H)-one (1), has been isolated from the fruits of T. ruticarpum, together with eleven known compounds. The structure of the new compound was determined by NMR and MS analyses. Rutaecarpine (4), evodiamine (5), and skimmianine (7) exhibited inhibition (IC(50) < or = 20.9 microM) of O2(.-) generation by human neutrophils in response to N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB). In addition, 1, evocarpine (2), 4, 7, and evodol (8) inhibited fMLP/CB-induced elastase release with IC(50) values < or =14.4 microM.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
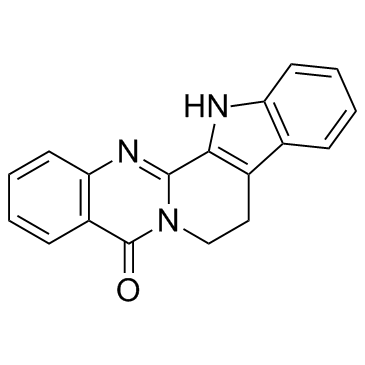 |
Rutaecarpine
CAS:84-26-4 |
C18H13N3O |
|
Pharmacological effects of rutaecarpine as a cardiovascular ...
2010-03-01 [Molecules 15(3) , 1873-81, (2010)] |
|
Transdermal behaviors comparisons among Evodia rutaecarpa ex...
2012-07-01 [Fitoterapia 83(5) , 954-60, (2012)] |
|
Effects of rutaecarpine on the metabolism and urinary excret...
2011-01-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 34(1) , 119-25, (2011)] |
|
Synthesis and biological properties of benzo-annulated rutae...
2010-01-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 33(10) , 1704-9, (2010)] |
|
Rutaecarpine prevents hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced myocardi...
2011-03-01 [Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 89(3) , 177-86, (2011)] |