| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
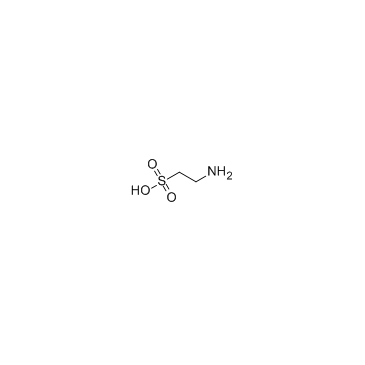 |
Taurine
CAS:107-35-7 |
|
 |
Forskolin
CAS:66575-29-9 |
|
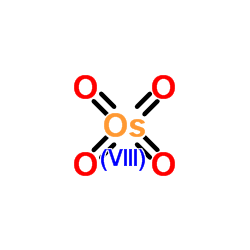 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
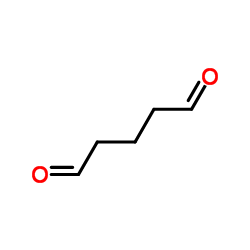 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
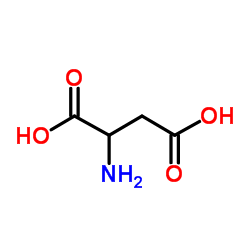 |
DL-Aspartic Acid
CAS:617-45-8 |
|
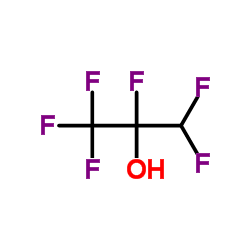 |
Hexafluoroisopropanol
CAS:920-66-1 |
|
 |
Thiocarbohydrazide
CAS:2231-57-4 |