| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
S-(2-Aminoethyl)-L-cysteine hydrochloride
CAS:4099-35-8 |
|
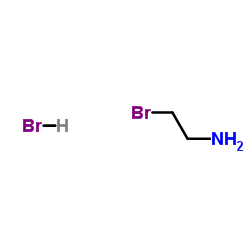 |
2-Bromoethylamine hydrobromide
CAS:2576-47-8 |