| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
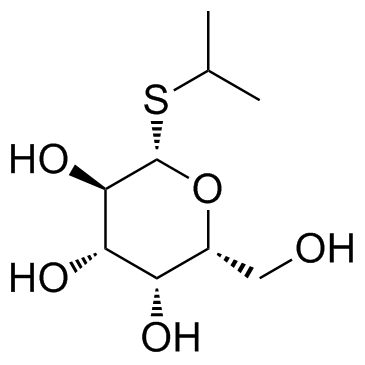 |
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
 |
Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium
CAS:102029-73-2 |
|
 |
Succinyl-Coenzyme A (sodium salt)
CAS:108347-97-3 |