A confocal study on the visualization of chromaffin cell secretory vesicles with fluorescent targeted probes and acidic dyes.
Alfredo Moreno, Jaime SantoDomingo, Rosalba I Fonteriz, Carmen D Lobatón, Mayte Montero, Javier Alvarez, Alfredo Moreno, Jaime SantoDomingo, Rosalba I. Fonteriz, Carmen D. Lobatón, Mayte Montero, Javier Alvarez
Index: J. Struct. Biol. 172(3) , 261-9, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Secretory vesicles have low pH and have been classically identified as those labelled by a series of acidic fluorescent dyes such as acridine orange or neutral red, which accumulate into the vesicles according to the pH gradient. More recently, several fusion proteins containing enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and targeted to the secretory vesicles have been engineered. Both targeted fluorescent proteins and acidic dyes have been used, separately or combined, to monitor the dynamics of secretory vesicle movements and their fusion with the plasma membrane. We have now investigated in detail the degree of colocalization of both types of probes using several fusion proteins targeted to the vesicles (synaptobrevin2-EGFP, Cromogranin A-EGFP and neuropeptide Y-EGFP) and several acidic dyes (acridine orange, neutral red and lysotracker red) in chromaffin cells, PC12 cells and GH(3) cells. We find that all the acidic dyes labelled the same population of vesicles. However, that population was largely different from the one labelled by the targeted proteins, with very little colocalization among them, in all the cell types studied. Our data show that the vesicles containing the proteins more characteristic of the secretory vesicles are not labelled by the acidic dyes, and vice versa. Peptide glycyl-L-phenylalanine 2-naphthylamide (GPN) produced a rapid and selective disruption of the vesicles labelled by acidic dyes, suggesting that they could be mainly lysosomes. Therefore, these labelling techniques distinguish two clearly different sets of acidic vesicles in neuroendocrine cells. This finding should be taken into account whenever vesicle dynamics is studied using these techniques.Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
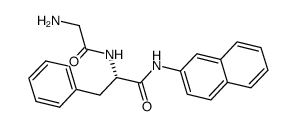 |
H-Gly-Phe-βNA
CAS:21438-66-4 |
C21H21N3O2 |
|
Effect of glycyl-L-phenylalanine 2-naphthylamide on invertas...
1985-02-01 [Biochem. J. 225(3) , 645-8, (1985)] |
|
Constitutive lysosome exocytosis releases ATP and engages P2...
2012-10-01 [J. Cell Sci. 125(Pt 19) , 4567-75, (2012)] |
|
Calcium mobilization by nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide ...
2006-02-01 [Cell Calcium 39(2) , 143-53, (2006)] |
|
N-acetylneuraminic acid accumulation in a buoyant lysosomal ...
1986-09-14 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 139(2) , 838-44, (1986)] |
|
Expression and purification of active recombinant cathepsin ...
2009-01-01 [J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009 , 746289, (2009)] |